Robotic designs use open and closed chain mechanisms to transmit motion from the actuators to an end-effector. Studies focus on kinematics, dynamics, and synthesis of such mechanisms.
Image Carousel with 5 slides
A carousel is a rotating set of images. Use the previous and next buttons to change the displayed slide
-
Slide 1: C-ALEX
-
Slide 2: Neck Brace Design
-
Slide 3: RoSE Schematic
-
Slide 4: RoSE Design Process
-
Slide 5: Book: Kinematics, Dynamics, and Design of Machinery
C-ALEX
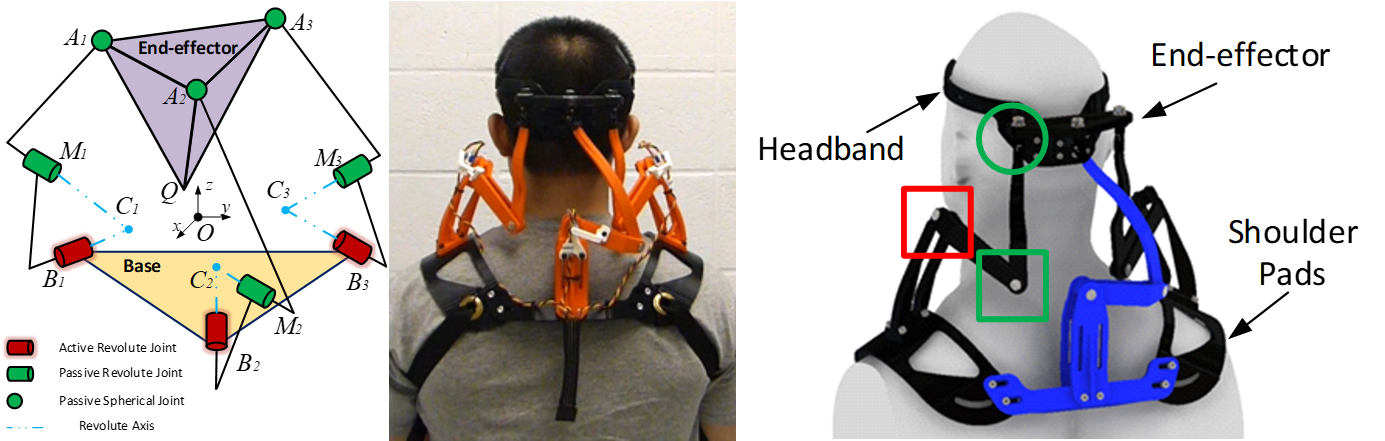
Neck Brace Design
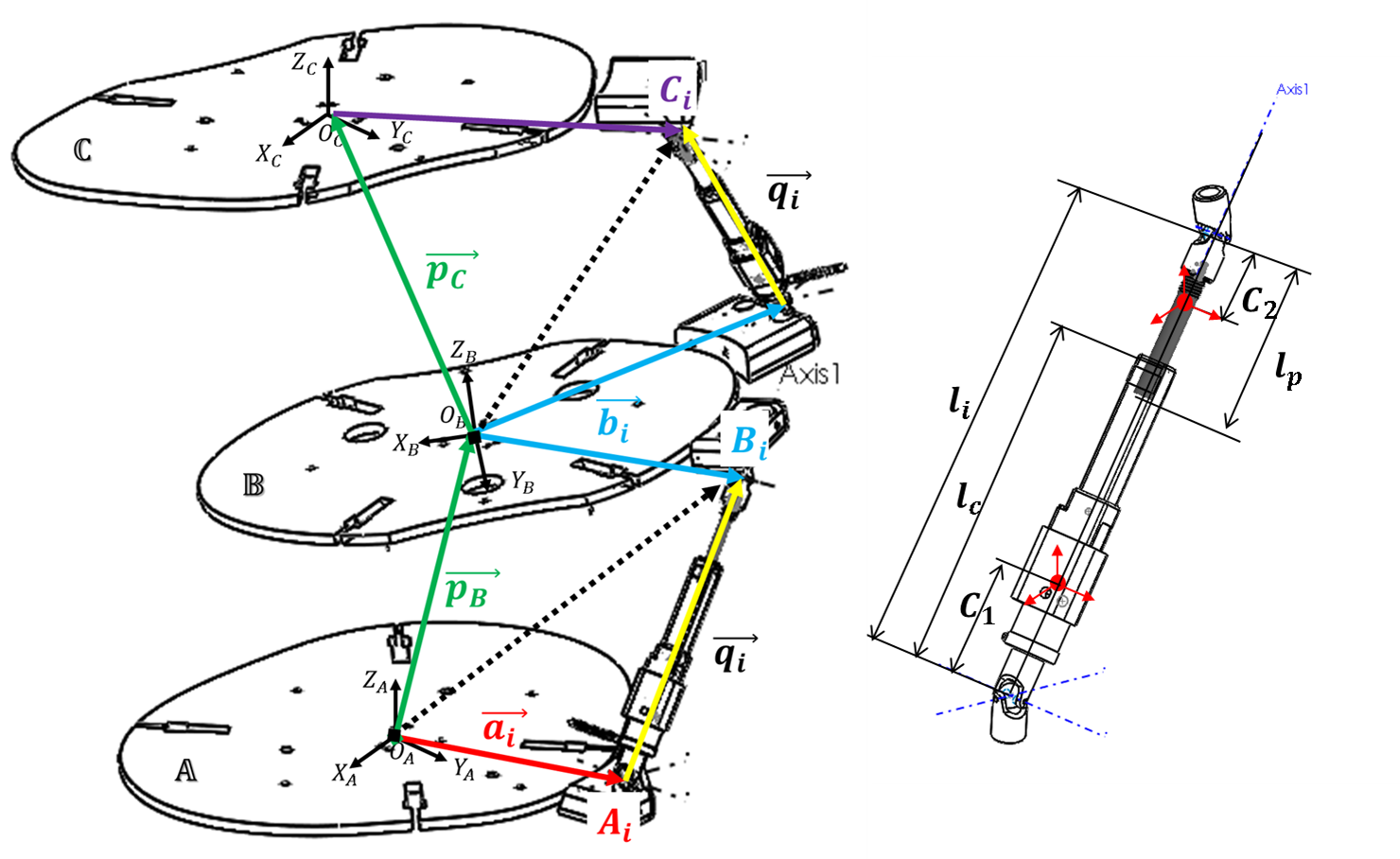
RoSE Schematic
RoSE Design Process

Book: Kinematics, Dynamics, and Design of Machinery
Parallel Actuated Robots

Kinematics, Dynamics, and Design of Machinery, Third Edition, discusses techniques for mechanism design, chiefly rational synthesis and kinematic analysis. It presents a fresh approach to the topic and is suitable for graduate and senior undergraduate students.
Several of the designs in our lab incorporate cable-driven systems, which pose unique design challenges. Part of our work involves developing new methods for the design and optimization of these systems in order create reliable devices that interact well with human subjects.
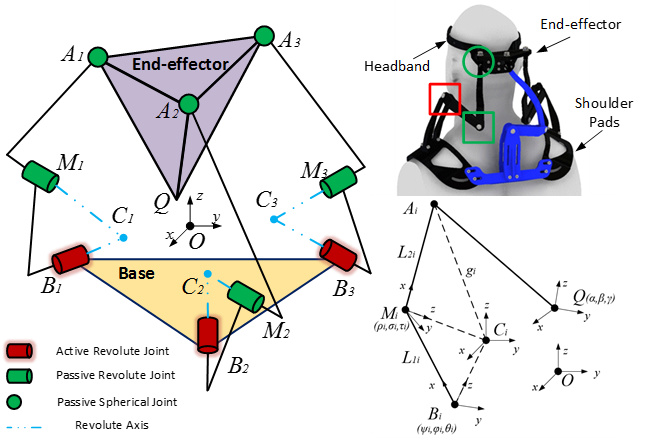
The underlying architecture is 3-RRS mechanism, as shown in Fig. 1. One can regard this mechanism as a perturbation from the well-known 3-RRS spherical mechanism, where all revolute axes intersect at a point, resulting the end-effector performs a spherical motion. Since the motion of a human head is not purely spherical, the 3-RRS wrist cannot deliver the desired motion. Thus, we modified the spherical mechanism by separating the intersecting points into three, one for each chain. In this case, the end-effector obtains a motion with coupled rotation and translation.
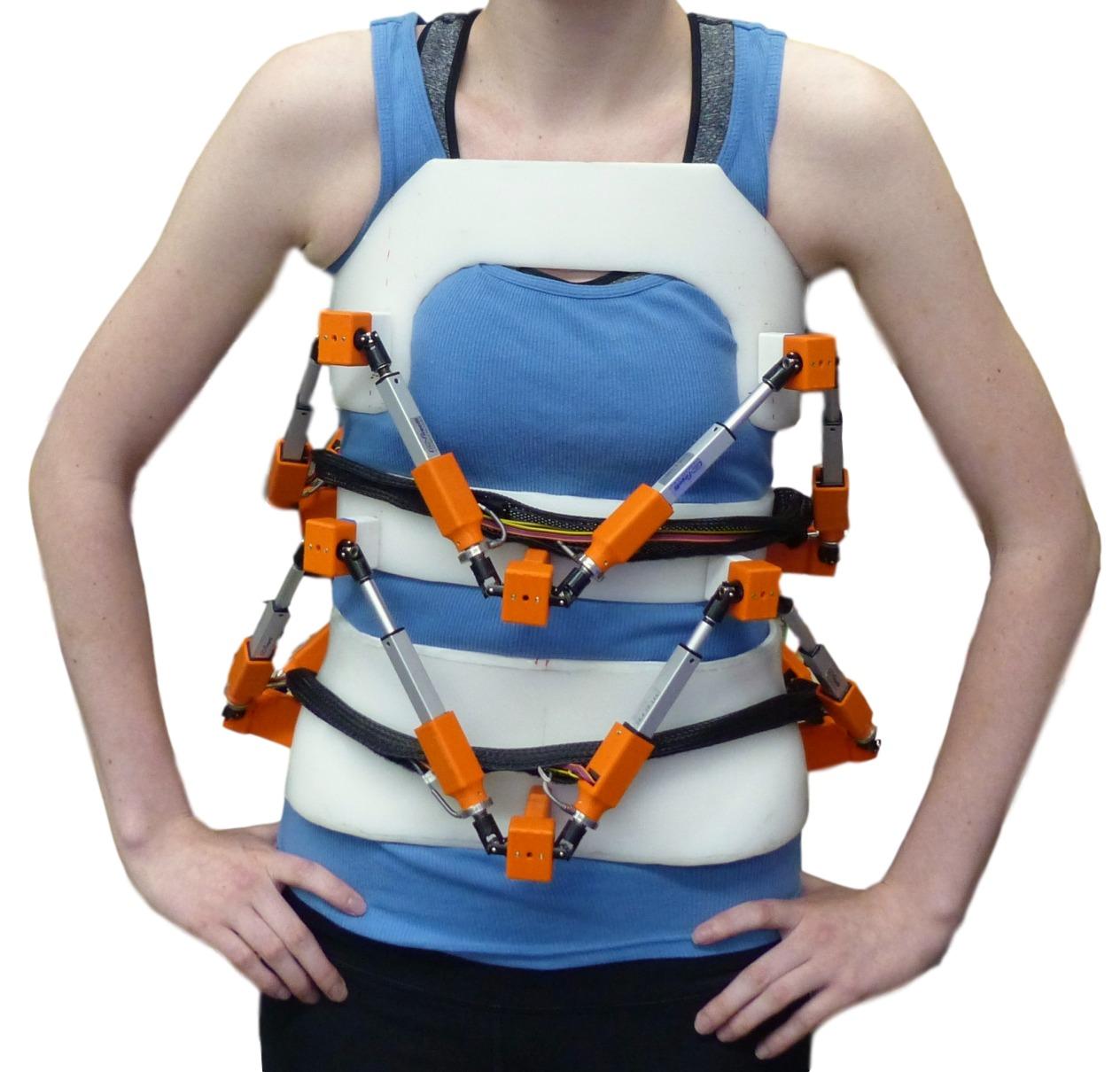
The RObotic Spine Exoskeleton is a two-layer Stewart platform, each layer consisting of a six degree-of-freedom spatial parallel mechanism.
